How has the profile of non-resident foreigners who buy homes in Spain changed?
The demand for housing among non-resident foreign buyers has grown sharply in recent years, especially after the pandemic, consolidating itself as one of the main drivers of Spain's real estate market. This boom is a response to several attractions which Spain has to offer, such as economic stability, the perception of security, good connectivity and a real estate offer that remains competitive. The profile of these buyers and the areas of interest have diversified, with an increase in the variety of nationalities and chosen locations: the influence of the United Kingdom has reduced, Poland is in the top 5 buyer nationalities, interest from the US and Latin America is on the rise, and new centres of interest are emerging in less traditional areas, such as Castellón, Asturias, Huelva and Córdoba.
The boom in house sales in Spain to non-resident foreign buyers
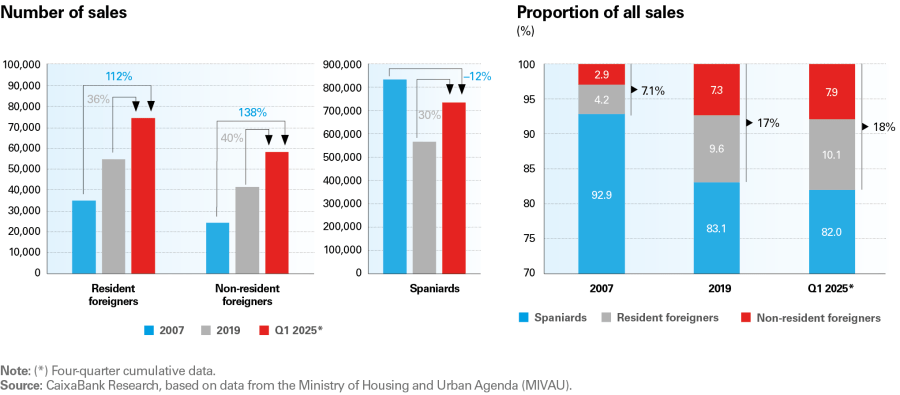
The demand for housing in Spain among foreigners has grown sharply since the pandemic and, more recently, it has been once again driven by improved financing conditions. According to data on real estate transactions from the Ministry of Housing and Urban Agenda (MIVAU), some 133,000 homes were acquired by foreign buyers in the trailing 12 months to Q1 2025, representing 18.0% of the total. This is 37.9% more transactions than in 2019 and marks a peak in the historical series, which dates back to 200612,13 In comparison, sales to Spaniards are «only» 28.0% above the 2019 level and have not exceeded the peak of 2006-2007, highlighting the key role of foreign demand in the current expansive cycle.
Much of this demand comes from foreigners residing in Spain, a group that has been growing in recent years as a result of the considerable influx of immigrants into our country.114 Specifically, residents accounted for 56.2% of total sales to foreigners in Q1 2025 (four-quarter cumulative data), representing 10.1% of total sales compared to 9.6% in 2019. This group, generally speaking, tends to acquire a home in Spain for work or educational reasons, among others. In fact, they share a very similar purchasing pattern to that of Spanish residents in key aspects such as location (usually in urban areas), the type of housing acquired (similar average price) and the frequent use of financing to make the purchase.15
- 12
According to the Association of Property Registrars, sales to foreign buyers accounted for 14.4% of the total, or around 100,000 sales, in the trailing four quarters to Q2 2025. In this article, we use MIVAU and Notary data because they distinguish between resident and non-resident foreigners.
- 13
The historical average share of all sales made to foreign buyers is 14.9% in the period 2006-2024.
- 14
According to data from the Continuous Population Statistics, Spain’s population has increased by around
2 million people between Q4 2019 and Q2 2025, 1.8 million of which are foreign nationals. - 15
See «Foreigners’ appetite for homes in Spain since the pandemic», available in the Monthly Report of January 2025.
Home sales according to the buyer’s residence and nationality
However, the demand for housing among non-resident foreigners is the category that has increased the most as a proportion of total sales, whether we compare it to before the pandemic (+0.6 pps, going from 7.3% in 2019 to 7.9% in Q1 2025) or relative to the previous expansionary cycle, when this group accounted for just 2.9% of total sales in 2007.
These buyers have a clearly distinct profile from residents. Generally, they acquire homes to spend their holidays in or as investments. They tend to have a higher purchasing capacity, which leads them to prefer touristic locations and mid-high or high-end properties. This trend directly influences demand in certain areas, especially those which appeal to tourists or offer a good potential return. Thus, the average price per square metre of the homes acquired by non-residents was 3,063 euros/m² in S2 2024, compared to 1,795 euros/m² in the case of resident foreigners and 1,713 €/m² for nationals. In addition, the increase in the average price at which non-residents have been buying homes in recent years has been much more pronounced, at 38% since 2019 (see chart below). In part, this trend reflects the fact that Spain has consolidated its position as one of the most attractive destinations for investment in luxury properties in Europe.
Next, we will focus on this group, because it is the one that has grown the most in recent years and because of the transformation it has experienced compared to previous decades. This surge in non-resident foreign buyers in Spain’s property market can be attributed to a variety of factors, ranging from the current strength of the Spanish economy, the perception of security and geopolitical stability with respect to other destinations and the fact that, despite the recent rally, house prices remain more competitive than in the main foreign buyers’ countries of origin.
The United Kingdom continues to lead, although its influence has reduced, while other nationalities are increasing their presence
Next, we analyse the changes in the nationalities of these buyers, comparing their share of the total in the recent period (average for 2020-2024) with the previous decade (2010-2019). During these two periods in question, sales to non-resident foreigners have increased from an average of 33,000 transactions per year to 48,000 in the more recent period, while their share of total sales has increased from 8.2% to 9.6%.
The United Kingdom remains the main country of origin for non-resident foreign buyers, but its share has declined significantly in the post-pandemic period: it has gone from accounting for 22% of sales transactions in 2010-2019 to around 15% in the more recent period (a fall of 7 pps). This downward trend is largely explained by the impact of Brexit, the depreciation of the pound and the modest performance of the country’s economy since the pandemic. In any event, it should be noted that the number of sales to British buyers has remained fairly stable between these two periods, at around 7,400 transactions per year; in fact, the fall in the United Kingdom’s share reflects the boom in purchases by other nationalities, as we will see below.
Countries such as Germany, Belgium and the Netherlands have seen their share increase and have established themselves as key actors in the demand for housing among non-resident foreigners. Special mention should be made of German buyers, to whom the number of sales has increased the most in absolute terms, by around 3,300 annually between these two periods, and with just under 7,000 sales they are now catching up on the British. On the other hand, France and Sweden have seen their share of total purchases decline slightly in recent years, although they remain high up in the ranking (in third and sixth positions, respectively, in the period 2020-2024 on average). Moreover, the number of sales to these nationalities has increased between these two periods (an additional 1,000 per year in the case of the French and around 250 for the Swedes).16
Poland is the nationality that has increased its share of the total the most between these two periods: going from representing just 0.7% of the total in the decade prior to the pandemic, to 4.7% in 2020-2024. This upward trend has allowed it to climb to fifth position in the ranking in 2024, surpassing Sweden and France.
Although they are not among the main players, it is worth noting the growing interest of buyers from Ukraine, Romania, Ireland and Portugal. This phenomenon reflects a gradual diversification in the profile of foreign buyers, possibly linked to factors such as intra-European mobility, the digitalisation of work and the international perception of high public safety compared to other countries, especially with the war in Ukraine (this factor could explain the upsurge in Eastern European buyers, including Polish citizens).
Outside the European sphere, we also note an increase in interest from US buyers, a phenomenon that seems to go hand in hand with the sharp increase in American tourism since the pandemic.17 There is also a growing presence of non-resident Latin American buyers, especially from Argentina, Colombia and Venezuela. Although their share of total sales is still modest, the growth is significant: together, they now represent around 1% of the sales of this group, compared to 0.5% in the previous decade.
- 17
Arrivals of American tourists visiting Spain have skyrocketed in the post-pandemic period, increasing by no less than 1 million tourists, to 4.3 million, between 2019 and 2024. Recently, there has been a marked slowdown in tourism spending from the US, affected by economic uncertainty, the depreciation of the dollar and the country’s lower growth. See the article «Uncertainty and US tourism», published in the Tourism Sector Report S2/2025.
Main non-resident foreign buyers in the Spanish housing market
Which provinces are the most attractive to non-resident international buyers?
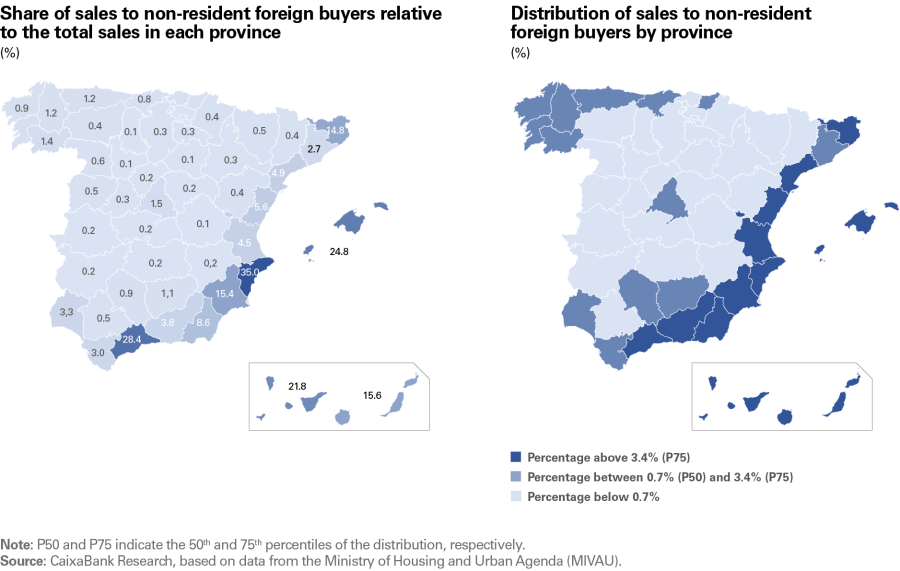
The following maps, based on cumulative four-quarter data to Q1 2025, show: (1) the share of total sales attributable to non-resident foreign buyers in each province and (2) the distribution of the total sales to foreigners by province. It can be seen how the provinces that are most attractive to non-resident foreign buyers are mainly concentrated along the Mediterranean arc and in the island regions. These coastal areas, of marked touristic character, have traditionally been the ones in most demand among this group of buyers, due to their benign climate, their wide range of leisure activities and services, and their good connectivity by air with the main European countries. In addition, factors such as the quality of life, the presence of established international communities and the availability of housing geared towards the international market reinforce its attractiveness as a preferred destination for buying second homes or real estate investments.
The first map shows the relevance of non-resident foreign buyers in some provinces where they represent a significant portion of the total. The most notable are Alicante (35% of all sales in the province), Malaga (28%), the Balearic Islands (25%), Santa Cruz de Tenerife (22%), Las Palmas (15%), Murcia (15%) and Girona (15%).
In the second map, which shows the national distribution of sales to non-resident foreigners by province, we can see that the highest percentage of sales is concentrated in the provinces that make up the Mediterranean arc, the islands and some Andalusian provinces (the dark blue colour shows those with a percentage greater than 3.4%, corresponding to the 75th percentile of the distribution). However, the interest of international buyers extends to other areas too. In an intermediate position we find areas such as the north-west of Spain – all the Galician provinces, Asturias, Cantabria and the north of the Basque Country – where, despite not being mass tourist destinations, the role of non-resident foreign buyers exceeds the national average. Madrid, which also holds an intermediate position, deserves a special mention, since despite not being a beach destination, being the capital city its role as a business centre and its extensive range of cultural and leisure activities make it a pole of attraction for international buyers. At the opposite end of the spectrum, the provinces of Spain’s interior make up a much smaller share of the total (light blue colours, below 0.7%), probably due to their less touristic tradition and their more limited international connectivity.
Housing sales to non-resident foreign buyers (Q1 2025)
The growing role of American buyers is key in five regions
The following maps show the top nationality in each autonomous community in home sales involving a non-resident foreign buyer in 2019 and 2024. Firstly, we note how the waning role of British buyers has major regional repercussions: whereas just prior to the pandemic this nationality was the main buyer in four communities (Murcia, Andalusia, Valencia and Asturias), today it only remains the top buyer in Murcia and Andalusia, and its share of total sales has reduced significantly in both cases.
In the case of German buyers, despite having significantly increased the number of transactions and their share of total sales across Spain as a whole, their influence is concentrated in the island regions: in the Balearic Islands and the Canary Islands they account for over half of all purchases by non-resident foreigners, and in the Canary Islands in particular this share has surged (from 21% in 2019 to 55% in 2024). In 2019, however, they were the main buyers in four more regions: Galicia, Cantabria, the Basque Country and Aragon.
The presence of French buyers in the country has diversified while American buyers have emerged as a major force
Unlike German buyers, French buyers have reduced their share of total purchases, but they remain the main nationality in five autonomous communities (Catalonia, Cantabria, Castile and León, Aragon and Navarre). That said, in general their share of the total has decline, which once again reveals a greater diversification of the nationalities buying housing in Spain.
Finally, there is a growing influence of non-resident buyers from the US in Spain’s housing market: although in the country as a whole they represent only 2.6% of all sales to this group, they are the top buyers in five Spanish autonomous communities in 2024, whereas at the end of 2019 the US was not the main buyer in any: the Basque Country, La Rioja, Asturias, Galicia and Castilla-La Mancha.
Share of unsubsidised home sales to non-resident foreign buyers by autonomous community
Territorial dynamics of sales to non-residents: Which destinations are gaining or losing appeal?
In order to identify changes in the demand from this type of buyer, we analysed trends in the share of sales made to non-resident foreign buyers between Q4 2019 and Q1 2025 (in both cases, cumulative 12-month data). The charts below show the 10 provinces that have gained the most appeal for this type of buyer in this period and the 10 that have lost the most appeal. This comparison allows us to detect relevant territorial dynamics and anticipate potential trends in international demand.
Broadly speaking, the provinces that have generated the most interest in recent years are locations that have been traditionally attractive to international buyers. Of particular note is Malaga, with 28.4% of all sales in the province, consolidating its position as the second most appealing province for this group of buyers behind only Alicante (35.0%), as well as the one that has gained the most appeal in the post-pandemic period. This growing interest is explained by its powerful appeal for tourism and, more recently, its significant growth as an economic centre: Malaga is positioning itself as a technological hub in southern Europe. In addition, it offers more competitive prices than Madrid or Barcelona and has excellent international connectivity, with direct flights to numerous European cities. Finally, the Balearic Islands, Santa Cruz de Tenerife and Murcia complete the ranking of provinces with increasing interest from non-resident foreign buyers.
Malaga, the Balearic Islands and Santa Cruz de Tenerife are the provinces that have generated the greatest interest since the pandemic
It is also worth mentioning other provinces where non-resident foreign buyers have traditionally played a minor role in the housing market, but which have seen a significant growth in their role in recent years, perhaps reflecting a change of trend in their preferences. Such provinces include Huelva, Orense and Lugo, which, despite not being consolidated tourist destinations, are gaining attraction thanks to factors such as more affordable prices, less saturation and a growing offer of housing geared towards international buyers. Madrid has also emerged as a location that has been generating significant interest since the pandemic.
At the other extreme, we note the loss of appeal of some provinces of Catalonia, such as Girona and Tarragona, which have seen a decline in the share of their sales to non-resident foreigners. This decrease is largely due to reduced interest on the part of French buyers, who have traditionally been very present in this area but have begun to diversify their interest in favour of other Spanish provinces.18 Some Andalusian provinces, such as Almeria and Granada, have also lost relative appeal, possibly to the benefit of other neighbouring provinces that have maintained their appeal or even seen it increase, such as Malaga and Murcia, among others.
- 18
According to data from the General Council of Notaries, French citizens accounted
for around half of all purchases in Catalonia in 2019, whereas they explained just 33% in 2024.
Girona, Tarragona, Almeria and Granada are the provinces that have seen the greatest loss of appeal among non-resident foreign buyers